태양풍에 대한 요약
태양풍에 대한 요약🌅
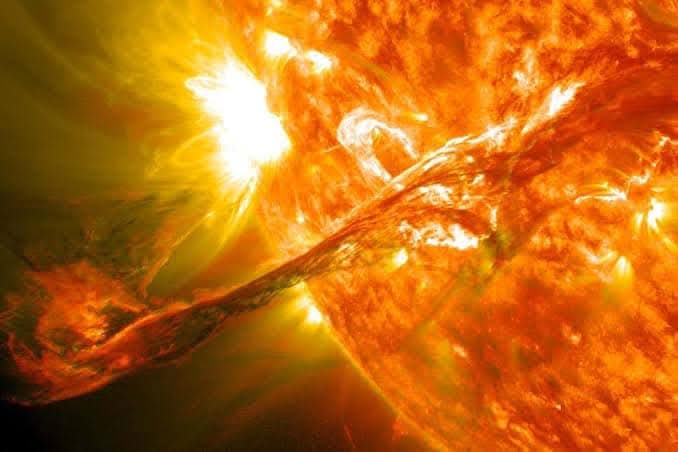

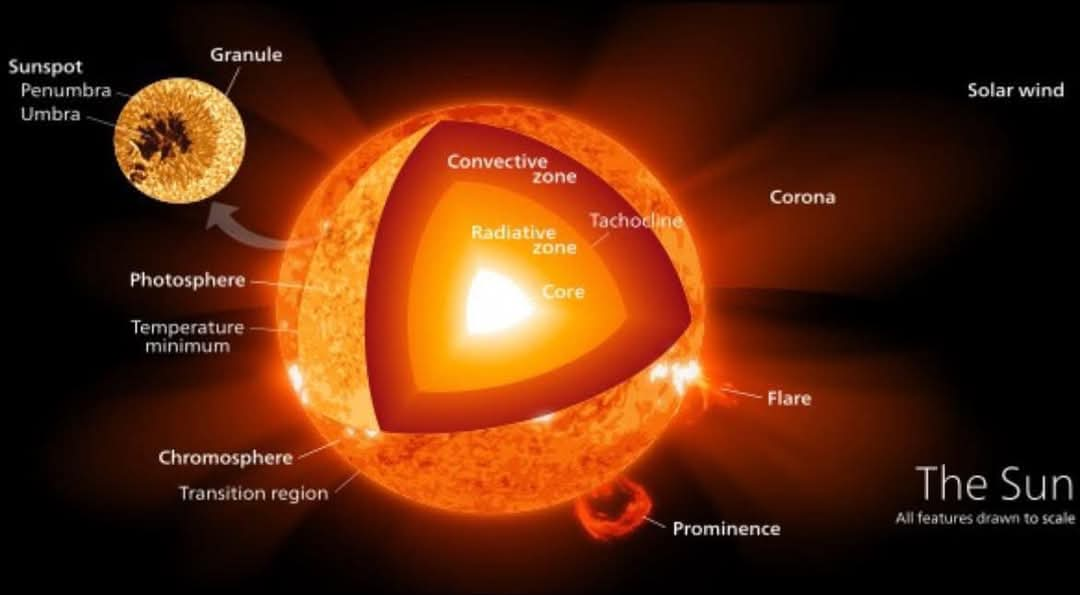
태양풍은 태양의 가장 바깥쪽 대기층인 코로나에서 방출되는 대전된 입자의 흐름입니다.
이 플라스마는 대부분 전자, 양성자 및 알파 입자로 구성되며 운동 에너지는 0.5~10 keV입니다.
태양풍 플라스마의 구성에는 태양 플라스마에서 발견되는 입자 종의 혼합물도 포함됩니다. 탄소, 질소, 산소, 네온, 마그네슘, 실리콘, 유황 및 철과 같은 원소의 미량의 중이온과 원자핵입니다.
인, 티타늄, 크롬 및 니켈의 동위 원소인 58Ni, 60Ni 및 62Ni와 같은 다른 핵과 동위 원소의 더 드문 흔적도 있습니다.
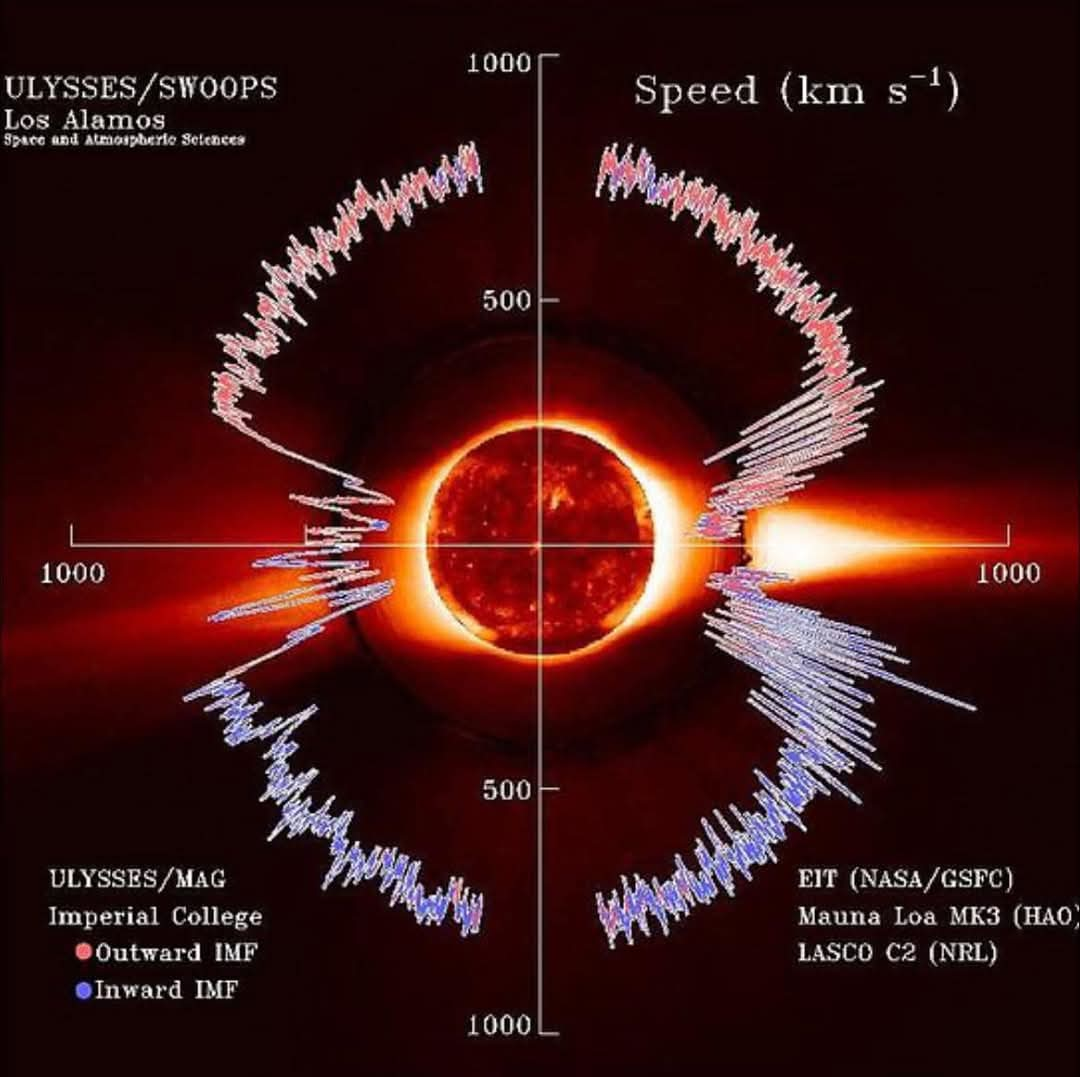
태양풍 플라스마와 중첩되는 것은 행성 간 자기장입니다.
태양풍은 시간과 태양 위도 및 경도에 따라 밀도, 온도 및 속도가 다릅니다. 그 입자는 코로나의 고온에서 발생하는 높은 에너지로 인해 태양의 중력에서 벗어날 수 있으며, 이는 코로나 자기장의 결과입니다.
코로나와 태양풍을 분리하는 경계를 알프벤 표면이라고 합니다.
태양으로부터 몇 태양 반경 이상 떨어진 곳에서 태양풍은 250~750km/s의 속도에 도달하고 초음속입니다. 즉, 빠른 자기파의 속도보다 빠르게 움직입니다.
태양풍의 흐름은 종단 충격에서 더 이상 초음속이 아닙니다.
다른 관련 현상으로는 오로라(북극광 및 남극광), 항상 태양에서 멀어지는 혜성 꼬리, 자기장 선의 방향을 바꿀 수 있는 지자기 폭풍이 있습니다.
@everyone
🌅A summary regarding Solar Wind🌅
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the corona.
This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between 0.5 and 10 keV.
The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of particle species found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, and iron.
There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as phosphorus, titanium, chromium, and nickel's isotopes 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni.
Superimposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field.
The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field.
The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface.
At a distance of more than a few solar radii from the Sun, the solar wind reaches speeds of 250–750 km/s and is supersonic, meaning it moves faster than the speed of fast magnetosonic waves.
The flow of the solar wind is no longer supersonic at the termination shock.
Other related phenomena include the aurora (northern and southern lights), comet tails that always point away from the Sun, and geomagnetic storms that can change the direction of magnetic field lines.
@everyone