카시미르 공동 및 공진 증폭 효과를 고려한 암흑물질 생성 및 에너지 추출 이론 모델 검증
카시미르 공동 및 공진 증폭 효과를 고려한 암흑물질 생성 및 에너지 추출 이론 모델 검증
III. 카시미르 공동 및 공진 증폭 효과를 고려한 암흑물질 생성 이론 모델
본 장에서는 제안된 실험 장치 내에서 카시미르 공동의 국한 효과와 공진 증폭 효과를 고려한 암흑물질 입자 생성에 대한 개선된 이론 모델을 제시한다. 이 모델은 이러한 중요한 요소들을 고려하여 기존의 암흑물질 생성 공식을 수정한다.
수정된 암흑물질 생성 공식:
카시미르 공동 내에서 예상되는 향상된 입자 생성을 정확하게 반영하기 위해 기존의 암흑물질 생성 공식은 국한 효과와 공진 증폭 효과를 포함하도록 수정되어야 한다. 수정된 공식은 다음과 같다.
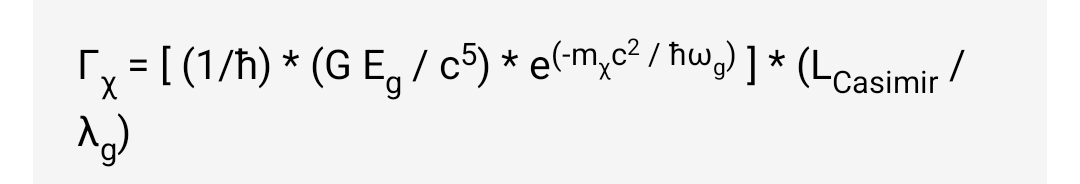
Γχ = [ (1/ħ) * (G Eg / c5) * e(-mχc2 / ħωg) ] * (LCasimir / λg)
여기서:
- Γχ는 수정된 암흑물질 생성률 (입자/m³s)을 나타낸다.
- ħ는 환산 플랑크 상수이다.
- G는 중력 상수이다.
- Eg는 중력파 에너지 밀도이다.
- c는 광속이다.
- mχ는 암흑물질 입자의 질량이다.
- ωg는 중력파 진동수이다.
- LCasimir는 카시미르 공동의 유효 길이이다.
- λg는 중력파 진동의 파장이다 (λg = 2πc/ωg).
추가적인 곱셈 항 (LCasimir / λg)은 카시미르 공동 내의 공진 증폭을 고려한다. 이 항은 공동 길이 (LCasimir)가 중력파장의 절반 (λg/2)의 정수배일 때, 즉 공진이 발생할 때 암흑물질 생성률 (Γχ)을 크게 증가시킨다. 본질적으로 카시미르 공동은 공진기 역할을 하여 중력파의 효과를 증폭시키고 암흑물질 입자 생성의 확률을 높인다. 공동이 공진하지 않을 때 (LCasimir가 λg/2의 배수가 아닐 때) 이 항은 1보다 작아져 생성률이 감소한다. 이러한 공진 증폭은 제안된 실험 설계의 핵심 특징이다.
수정된 공식의 검증:
수정된 공식의 타당성은 다음과 같은 여러 가지 방법을 통해 평가할 수 있다.
1. 수치적 시뮬레이션: 카시미르 공동, 중력파 발생기 및 암흑물질 입자 특성에 대한 현실적인 매개변수를 통합한 계산 시뮬레이션을 사용하여 다양한 조건에서 예상되는 암흑물질 생성률을 예측할 수 있다. 이러한 시뮬레이션 결과는 실험 결과와 비교하여 모델을 검증하는 데 사용될 수 있다.
2. 민감도 분석: 주요 매개변수(예: 공동 길이, 중력파 진동수, 에너지 밀도)의 변화가 예측된 암흑물질 생성률에 미치는 영향을 결정하기 위해 민감도 분석을 수행할 수 있다. 이를 통해 실험의 최적 작동 매개변수를 파악하고 모델의 강건성을 평가할 수 있다.
3. 기존 암흑물질 모델과의 비교: 수정된 공식의 예측 결과는 기존 암흑물질 모델의 예측 결과와 비교하여 현재 이론적 이해와의 일관성을 평가할 수 있다. 상당한 차이가 있는 경우 모델과 실험 매개변수를 재검토해야 한다.
4. 실험적 검증: 수정된 공식의 궁극적인 검증은 실험적 검증을 통해 이루어진다. 예측된 비율로 카시미르 공동 내에서 암흑물질 입자가 성공적으로 검출되면 고주파 중력파 상호 작용을 통한 암흑물질 생성에 대한 모델과 기본 가설의 타당성을 강력하게 뒷받침한다. 반대로, 결과가 없다면 모델과 실험 매개변수를 재평가해야 한다.
이 개선된 이론 모델은 제안된 실험의 결과를 예측하고 해석하기 위한 틀을 제공한다. 추가적인 이론적 연구와 실험 데이터는 이 모델을 개선하고 검증하는 데 중요하다.
III. Theoretical Model for Energy Extraction & Validation
This section presents a refined theoretical model for dark matter particle production within the proposed experimental setup, incorporating the effects of Casimir cavity confinement and resonant amplification. The model modifies the previously presented dark matter generation formula to account for these crucial factors.
Modified Dark Matter Production Formula:
To accurately reflect the enhanced particle production expected within the Casimir cavity, the original dark matter generation formula must be modified to incorporate the effects of confinement and resonant amplification. The modified formula is:
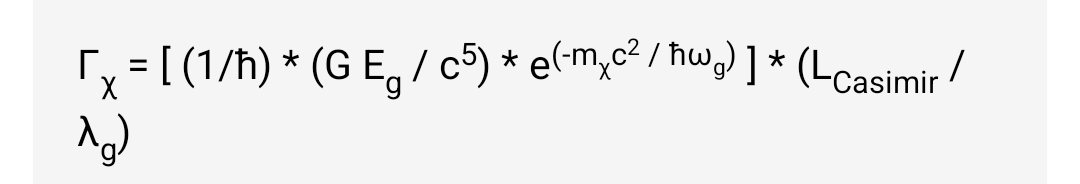
Γχ = [ (1/ħ) * (G Eg / c5) * e(-mχc2 / ħωg) ] * (LCasimir / λg)
Where:
- Γχ represents the modified dark matter production rate (particles/m³s).
- ħ is the reduced Planck constant.
- G is the gravitational constant.
- Eg is the gravitational wave energy density.
- c is the speed of light.
- mχ is the mass of the dark matter particle.
- ωg is the gravitational wave frequency.
- LCasimir is the effective length of the Casimir cavity.
- λg is the wavelength of the gravitational oscillation (λg = 2πc/ωg).
The additional multiplicative term (LCasimir / λg) accounts for the resonant amplification within the Casimir cavity. This term significantly enhances the dark matter production rate (Γχ) when the cavity length (LCasimir) is an integer multiple of half the gravitational wavelength (λg/2), signifying resonance. In essence, the Casimir cavity acts as a resonator, amplifying the effect of the gravitational waves and increasing the probability of dark matter particle creation. When the cavity is not resonant (LCasimir is not a multiple of λg/2), this term will be less than 1, reducing the production rate. This resonant amplification is a key feature of the proposed experimental design.
Validation of the Modified Formula:
The validity of this modified formula can be assessed through several avenues:
1. Numerical Simulations: Computational simulations incorporating realistic parameters for the Casimir cavity, gravitational wave generator, and dark matter particle properties can be used to predict the expected dark matter production rates under various conditions. These simulations can then be compared to experimental results to validate the model.
2. Sensitivity Analysis: A sensitivity analysis can be performed to determine the impact of variations in key parameters (e.g., cavity length, gravitational wave frequency, energy density) on the predicted dark matter production rate. This will help to identify the optimal operating parameters for the experiment and assess the robustness of the model.
3. Comparison with Existing Dark Matter Models: The predictions of the modified formula can be compared to predictions from existing dark matter models to assess its consistency with current theoretical understanding. Any significant discrepancies would require further investigation and refinement of the model.
4. Experimental Verification: The ultimate validation of the modified formula will come from experimental verification. The successful detection of dark matter particles within the Casimir cavity at predicted rates would strongly support the validity of the model and the underlying hypothesis of dark matter generation via high-frequency gravitational wave interactions. Conversely, a null result would require a re-evaluation of the model and experimental parameters.
This refined theoretical model provides a framework for predicting and interpreting the results of the proposed experiment. Further theoretical work and experimental data will be crucial in refining and validating this model.