행렬의 유형들(matrix types)
matrix types
이 이미지는 다양한 유형의 행렬(matrix)에 대한 설명과 예시를 보여줍니다. 각 유형에 대한 자세한 설명은 다음과 같습니다.
1. 행렬(Matrix)
- 행렬은 행(row)과 열(column)로 구성된 숫자들의 집합입니다[__LINK_ICON].
- 행렬은 벡터들의 순서 있는 모임으로 생각할 수도 있습니다.
- 행렬의 차원은 열의 개수에 따라 결정됩니다. 예를 들어, 2차원 행렬은 두 개의 열을 가지고, 3차원 행렬은 세 개의 열을 가집니다.
2. 행렬 유형
- 행렬은 그 형태와 특징에 따라 여러 유형으로 분류됩니다.
- 행렬(Row Matrix): 한 개의 행으로 구성된 행렬입니다.
- 열렬(Column Matrix): 한 개의 열로 구성된 행렬입니다.
- 정방 행렬(Square Matrix): 행과 열의 개수가 같은 행렬입니다.
- 대각 행렬(Diagonal Matrix): 대각선 요소만 값을 가지고 나머지 요소는 모두 0인 행렬입니다.
- 스칼라 행렬(Scalar Matrix): 대각선 요소가 모두 같은 값을 가지고 나머지 요소는 모두 0인 행렬입니다.
- 영 행렬(Null Matrix): 모든 요소가 0인 행렬입니다.
- 단위 행렬(Identity Matrix): 대각선 요소는 1이고 나머지 요소는 모두 0인 행렬입니다.
- 상삼각 행렬(Upper Triangular Matrix): 대각선 아래 요소가 모두 0인 행렬입니다.
- 하삼각 행렬(Lower Triangular Matrix): 대각선 위 요소가 모두 0인 행렬입니다.
- 전치 행렬(Transpose Matrix): 행렬의 행과 열을 바꾼 행렬입니다.
- 대칭 행렬(Symmetric Matrix): 전치 행렬과 동일한 행렬입니다.
- 반대칭 행렬(Antisymmetric Matrix): 전치 행렬과 부호가 반대인 행렬입니다.
3. 행렬의 활용
- 행렬은 선형대수, 기하학, 통계학, 컴퓨터 과학 등 다양한 분야에서 활용됩니다.
- 선형대수에서는 행렬을 이용하여 선형 변환, 연립 방정식 풀이, 벡터 공간 등을 다룹니다.
- 기하학에서는 행렬을 이용하여 회전, 이동, 확대/축소 등의 변환을 표현합니다.
- 통계학에서는 행렬을 이용하여 데이터 분석, 회귀 분석, 분산 분석 등을 수행합니다.
- 컴퓨터 과학에서는 행렬을 이용하여 이미지 처리, 그래픽 처리, 인공지능 등을 구현합니다.
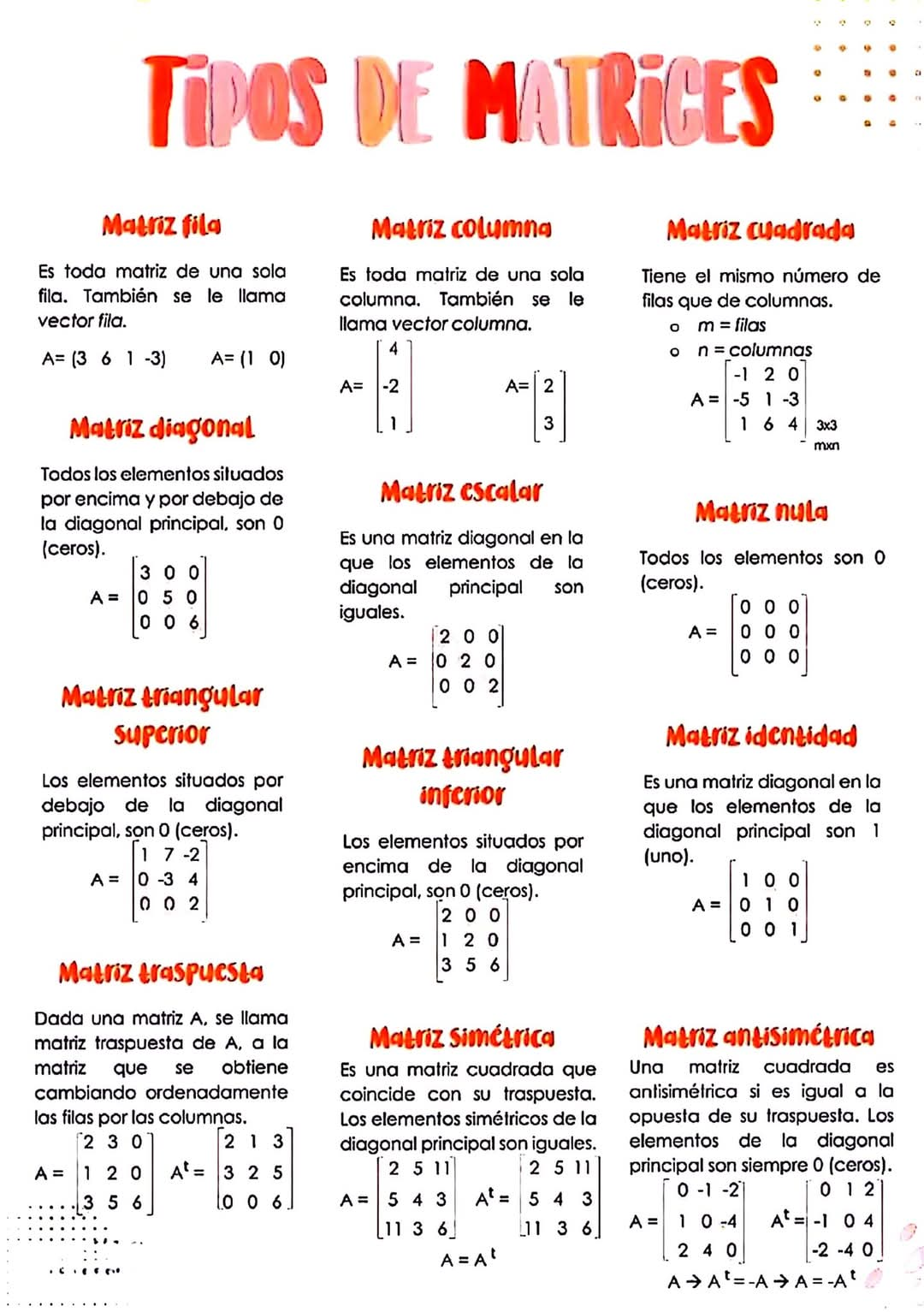
Here's a detailed explanation of the different types of matrices shown in the image, in English:
Detailed Explanation of Matrix Types
The image presents a chart explaining various types of matrices in mathematics, each with a description and example. Let's break down each type:
1. Matrix:
- A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns.
- Matrices are often used to represent linear transformations and systems of equations.
- The dimensions of a matrix are described by the number of rows and columns (e.g., a 3x2 matrix has 3 rows and 2 columns).
2. Types of Matrices:
The image categorizes matrices based on their structure and properties:
- Row Matrix: A matrix with only one row. Also called a row vector.
- Column Matrix: A matrix with only one column. Also called a column vector.
- Square Matrix: A matrix with an equal number of rows and columns.
- Diagonal Matrix: A square matrix where all elements outside the main diagonal (top-left to bottom-right) are zero.
- Scalar Matrix: A diagonal matrix where all elements on the main diagonal are the same.
- Null Matrix (Zero Matrix): A matrix where all elements are zero.
- Identity Matrix: A square matrix where all elements on the main diagonal are 1, and all other elements are 0. It acts as a multiplicative identity.
- Upper Triangular Matrix: A square matrix where all elements below the main diagonal are zero.
- Lower Triangular Matrix: A square matrix where all elements above the main diagonal are zero.
- Transpose Matrix: A matrix derived from another matrix by interchanging its rows and columns. The transpose of matrix A is denoted as AT.
- Symmetric Matrix: A square matrix that is equal to its transpose (A = AT). Elements symmetrically positioned across the main diagonal are equal.
- Antisymmetric (Skew-Symmetric) Matrix: A square matrix that is equal to the negative of its transpose (A = -AT). Elements on the main diagonal are always zero.
3. Applications of Matrices:
Matrices are fundamental tools in various fields:
- Linear Algebra: Used for linear transformations, solving systems of linear equations, eigenvalue problems, and vector space analysis.
- Computer Graphics: Representing transformations (rotation, scaling, translation) of objects in 2D and 3D space.
- Computer Science: Used in algorithms for image processing, machine learning, and data analysis.
- Statistics: Analyzing datasets, performing statistical modeling, and solving statistical problems.
- Physics and Engineering: Modeling physical systems, solving differential equations, and analyzing data from experiments.
This detailed explanation provides a comprehensive understanding of the matrix types illustrated in the provided image, along with their broader applications.