시공간 간격 (Spacetime Interval, ds²)
시공간 간격 (Spacetime Interval, ds²)
민코프스키 메트릭은 상대성이론에서 시공간의 거리를 측정하는 데 사용되는 수학적 도구입니다. 간단히 말해, 4차원 시공간에서 두 사건 사이의 "거리"를 계산하는 방법을 정의합니다.
핵심 개념:
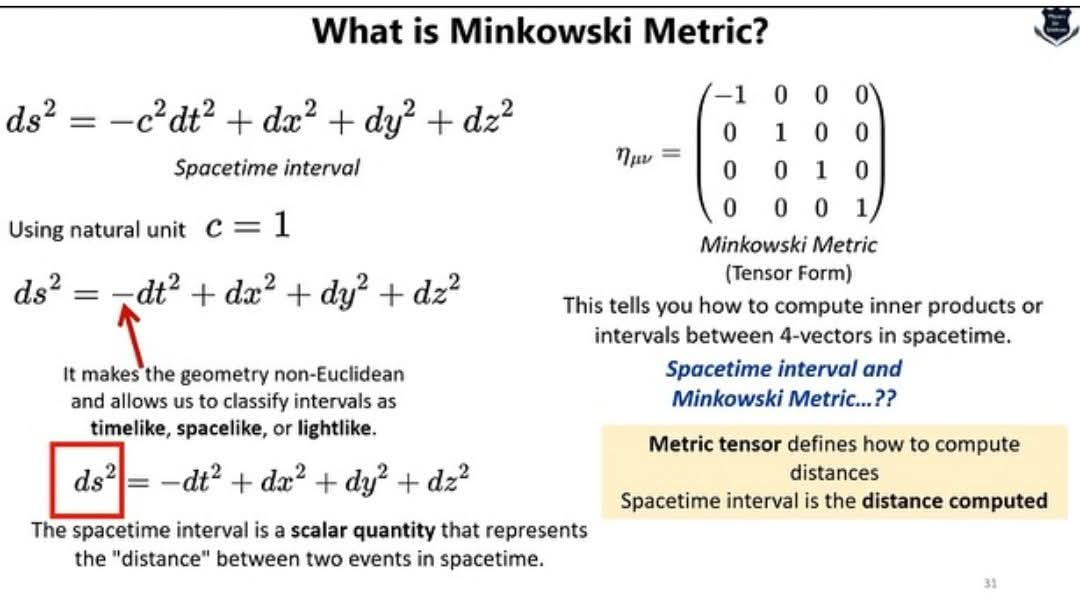
- 시공간 간격 (Spacetime Interval, ds²): 민코프스키 메트릭의 핵심은 시공간 간격입니다. 이는 두 사건 사이의 거리를 나타내는 스칼라량으로, 시간과 공간의 변화량을 결합하여 계산됩니다.
식은 다음과 같습니다.
ds² = -c²dt² + dx² + dy² + dz²
여기서:
- c : 빛의 속도
- dt : 시간 간격
- dx , dy , dz : 각 공간 축(x, y, z)의 변화량
- 자연 단위 (Natural Unit): 빛의 속도 c 를 1로 설정하면 식이 간단해집니다. ds² = -dt² + dx² + dy² + dz²
- 민코프스키 메트릭 (Minkowski Metric, ημν): 이는 텐서 형태로 표현되는 행렬로, 시공간 간격을 계산하는 방법을 정의합니다. 위의 이미지에서 보이는 행렬이 바로 민코프스키 메트릭입니다. 이 행렬을 이용하여 4차원 벡터(4-vector) 사이의 내적(inner product)을 계산할 수 있습니다.
- 간격의 분류 (Classification of Intervals): 시공간 간격의 부호에 따라 간격의 종류를 다음과 같이 분류합니다.
- 시간형 (Timelike): ds² < 0 두 사건 사이에 인과 관계가 있음을 의미합니다. 한 사건이 다른 사건에 영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
- 공간형 (Spacelike): ds² > 0 두 사건 사이에 인과 관계가 없음을 의미합니다. 한 사건이 다른 사건에 영향을 줄 수 없습니다.
- 광형 (Lightlike): ds² = 0 두 사건 사이를 빛이 이동하는 경로를 의미합니다.
민코프스키 메트릭의 중요성:
- 비유클리드 기하학 (Non-Euclidean Geometry): 민코프스키 메트릭은 유클리드 기하학과 다르게, 시간과 공간을 통합적으로 다루는 비유클리드 기하학을 사용합니다. 이는 특수 상대성이론의 기본 개념입니다.
- 상대성이론의 수학적 토대: 민코프스키 메트릭은 상대성이론의 수학적 토대를 제공하며, 시공간의 기하학적 성질을 이해하는 데 필수적입니다.
- 4차원 벡터의 연산: 4차원 벡터(4-vector) 사이의 내적을 계산하는 데 사용됩니다.
결론:
민코프스키 메트릭은 시공간의 거리를 측정하고, 사건 사이의 인과 관계를 분석하는 데 사용되는 중요한 수학적 도구입니다. 특수 상대성이론을 이해하는 데 필수적인 개념이며, 현대 물리학에서 널리 활용됩니다. 이 메트릭을 통해 우리는 유클리드 기하학으로는 설명할 수 없는 시공간의 비유클리드적 성질을 이해할 수 있습니다.

Spacetime Interval, ds²
The Minkowski metric is a mathematical tool used in relativity to measure distances in spacetime. Simply put, it defines how to calculate the "distance" between two events in four-dimensional spacetime.

Key Concepts:
- Spacetime Interval (ds²): The core of the Minkowski metric is the spacetime interval. This is a scalar quantity representing the distance between two events, combining changes in time and space. The equation is: ds² = -c²dt² + dx² + dy² + dz² where:
- c : the speed of light
- dt : the time interval
- dx , dy , dz : changes along each spatial axis (x, y, z)
- Natural Unit: Setting the speed of light c to 1 simplifies the equation: ds² = -dt² + dx² + dy² + dz²
- Minkowski Metric (ημν): This is a matrix represented in tensor form, defining how to compute the spacetime interval. This matrix is used to calculate the inner product between four-vectors (4-vectors).
- Classification of Intervals: The type of interval is classified based on the sign of the spacetime interval:
- Timelike: ds² < 0 Indicates a causal relationship between two events. One event can influence the other.
- Spacelike: ds² > 0 Indicates no causal relationship between two events. One event cannot influence the other.
- Lightlike: ds² = 0 Represents the path taken by light between two events.
Importance of the Minkowski Metric:
- Non-Euclidean Geometry: Unlike Euclidean geometry, the Minkowski metric uses a non-Euclidean geometry that integrates time and space. This is a fundamental concept in special relativity.
- Mathematical Foundation of Relativity: The Minkowski metric provides the mathematical foundation for relativity and is essential for understanding the geometric properties of spacetime.
- Operations on Four-Vectors: It's used to calculate the inner product between four-vectors.
Conclusion:
The Minkowski metric is a crucial mathematical tool used to measure distances in spacetime and analyze causal relationships between events. It's a fundamental concept in understanding special relativity and is widely used in modern physics. This metric allows us to understand the non-Euclidean nature of spacetime, which cannot be explained by Euclidean geometry.
참고 :
https://keeahsha.tistory.com/m/3937
슈바르츠실트 메트릭(Schwarzschild Metric)
Schwarzschild Metric (슈바르츠실트 메트릭)아래 이미지는 **슈바르츠실트 메트릭(Schwarzschild Metric)**을 시각적으로 그리고 수학적으로 보여줍니다. 일반 상대성 이론에서 중력을 시공간의 곡률로 설
keeahsha.tistory.com