전기 쌍극자에 의한 전기 전위
Electrical potential by electric dipole:
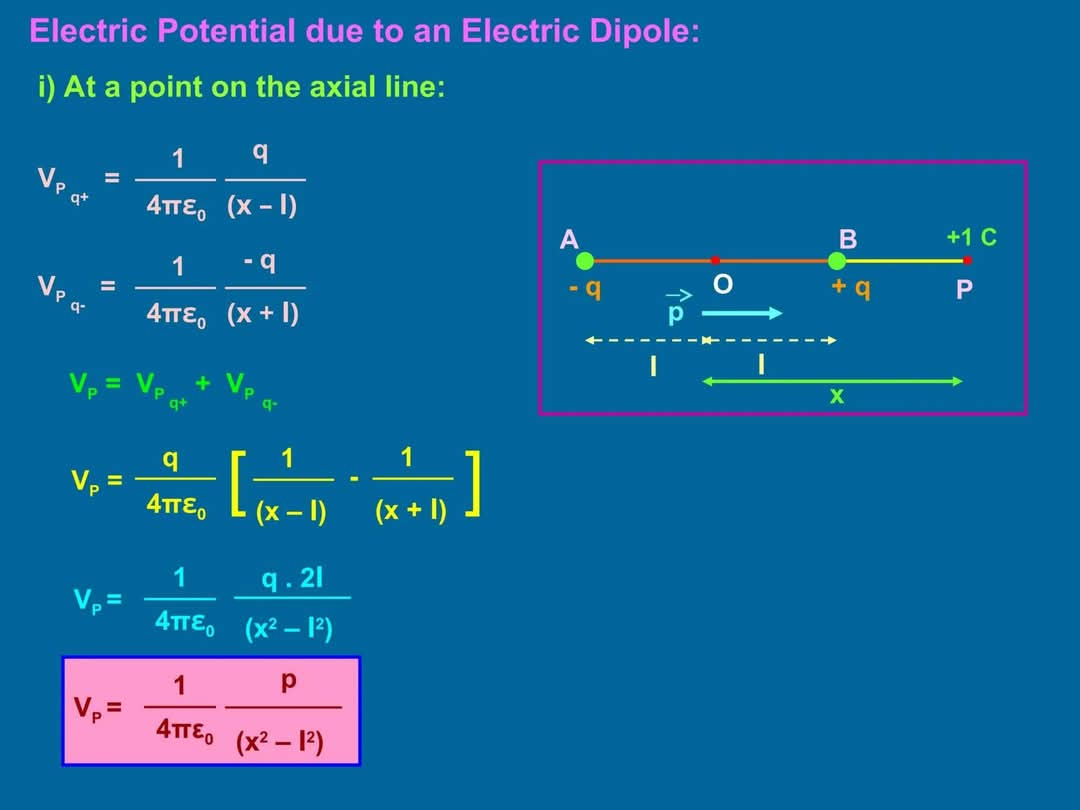
i) 축선상의 한 점에서:
- Vp+ = 1/(4πε0) * q/(x-l) : +q 전하에 의한 점 P에서의 전위. x는 점 P의 위치, l은 쌍극자의 절반 길이, ε0는 진공의 유전율, q는 전하량입니다. (x-l)은 +q 전하에서 점 P까지의 거리입니다.
- Vp- = 1/(4πε0) * -q/(x+l) : -q 전하에 의한 점 P에서의 전위. (x+l)은 -q 전하에서 점 P까지의 거리입니다. 음의 부호는 음전하임을 나타냅니다.
- Vp = Vp+ + Vp- : 점 P에서의 총 전위는 +q와 -q 전하에 의한 전위의 합입니다.
- Vp = q/(4πε0) * [1/(x-l) - 1/(x+l)] : 위의 식을 정리한 결과입니다.
- Vp = 1/(4πε0) * q.2l/(x² - l²) : 위 식을 더 간략하게 정리한 결과입니다. q.2l은 쌍극자 모멘트(p)와 같습니다.
참고 : 수식에서 q · 2l 중의 . 은 벡터의 내적(dot product) 또는 **스칼라곱(scalar product)**을 의미합니다.
- Vp = 1/(4πε0) * p/(x² - l²) : 쌍극자 모멘트 p를 사용하여 표현한 최종 공식입니다. x가 l보다 훨씬 클 때, l²은 무시할 수 있으므로 Vp ≈ 1/(4πε0) * p/x² 로 근사할 수 있습니다.
그림: 두 개의 점전하 (+q, -q)가 거리 2l만큼 떨어져 있는 쌍극자를 나타냅니다. 점 P는 쌍극자의 중심에서 x만큼 떨어진 축선상에 있습니다. O는 쌍극자의 중심점입니다.
요약: 이 이미지는 전기 쌍극자에 의해 축선상의 한 점에서 발생하는 전기 전위를 계산하는 방법을 보여주는 수식과 그림으로 구성되어 있습니다. 수식들은 점전하의 전위 공식을 이용하여 유도되었으며, 최종적으로 쌍극자 모멘트를 사용한 간결한 공식으로 나타낼 수 있습니다.
Electric Potential due to an Electric Dipole:
i) At a point on the axial line:
- Vp+ = 1/(4πε0) * q/(x-l): Electric potential at point P due to the positive charge (+q). Where: x is the distance of point P from the dipole's center, l is half the length of the dipole, ε0 is the permittivity of free space, and q is the magnitude of the charge. (x-l) represents the distance between the +q charge and point P.
- Vp- = 1/(4πε0) * -q/(x+l): Electric potential at point P due to the negative charge (-q). (x+l) is the distance between the -q charge and point P. The negative sign indicates a negative charge.
- Vp = Vp+ + Vp-: The total electric potential at point P is the sum of the potentials due to +q and -q charges.
- Vp = q/(4πε0) * [1/(x-l) - 1/(x+l)]: This is a simplified form of the previous equation.
- Vp = 1/(4πε0) * q.2l/(x² - l²): Further simplification of the equation. q.2l is equal to the dipole moment (p).
- Vp = 1/(4πε0) * p/(x² - l²): The final formula using the dipole moment p. When x is much larger than l, l² can be neglected, resulting in the approximation Vp ≈ 1/(4πε0) * p/x².
Diagram: The diagram shows an electric dipole with two point charges (+q, -q) separated by a distance of 2l. Point P lies on the axial line at a distance x from the center of the dipole. O represents the center of the dipole.
Summary: This image presents the derivation and final formula for calculating the electric potential at a point on the axial line of an electric dipole. The formulas are derived using the potential formula for point charges and simplified to a concise expression using the dipole moment.