전기쌍극자의 적도(수평방향)면 상 한 점에서의 전위를 계산하는 과정
Process for calculating the potential at a point on the equatorial (horizontal) plane of an electric dipole
아래 이미지의 수식은 전기쌍극자의 적도(수평방향)면 상 한 점에서의 전위를 계산하는 과정을 보여줍니다.
- VQ q+ 와 VQ q-: 각각 +q와 -q 전하가 점 Q에 만들어내는 전위입니다. 쿨롱의 법칙을 이용하여 계산됩니다. (1/(4πε₀))는 쿨롱 상수의 역수입니다. BQ와 AQ는 각각 +q와 -q 전하로부터 점 Q까지의 거리입니다.
- VQ = VP q+ + VP q-: 점 Q에서의 전체 전위는 각 전하가 만드는 전위의 합으로 구해집니다.
- VQ = q/(4πε₀) * [1/BQ - 1/AQ]: 위 두 식을 합쳐 간략하게 표현한 식입니다.
- VQ = 0 :: BQ = AQ: 적도면 상에서는 BQ와 AQ가 같으므로 (BQ = AQ), 전체 전위 VQ는 0이 됩니다. 즉, 쌍극자의 적도면 상의 임의의 점에서 전위는 0입니다.
요약하자면, 이미지는 쌍극자의 적도면에서 두 전하의 전위가 서로 상쇄되어 전체 전위가 0이 되는 것을 수학적으로 보여줍니다.
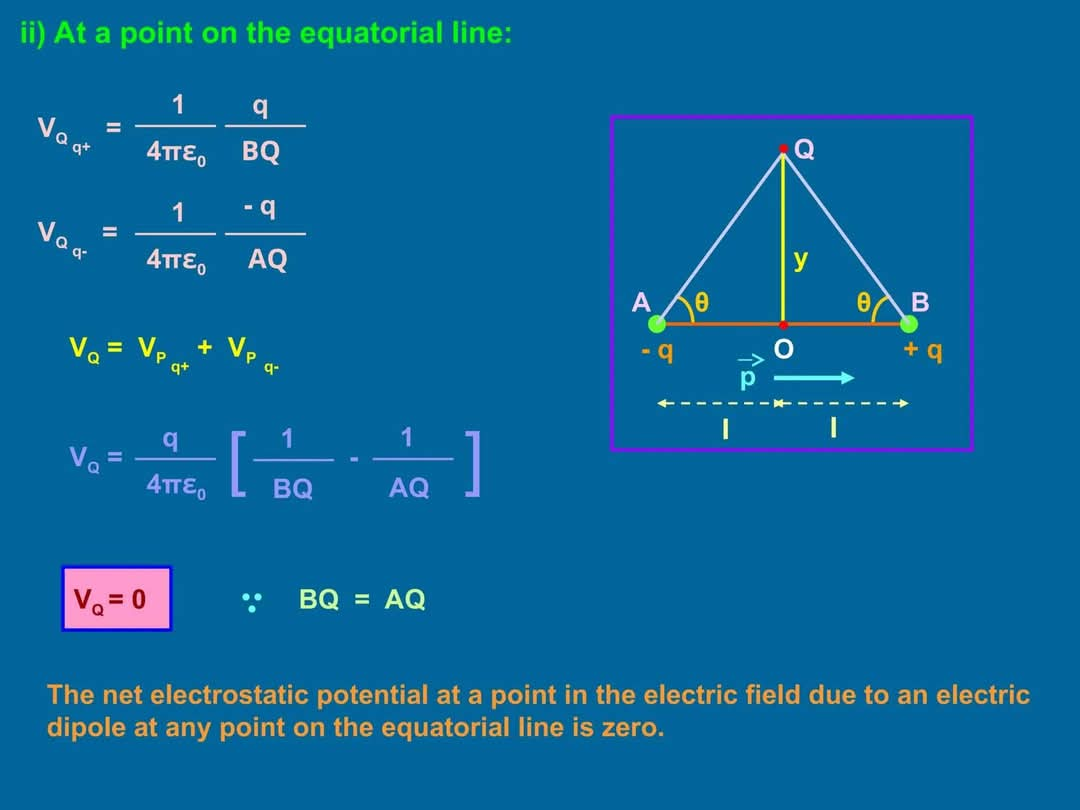
The image shows the calculation of the electric potential at a point on the equatorial plane of an electric dipole.
- VQ q+ and VQ q-: These represent the electric potentials at point Q due to the +q and -q charges, respectively. They are calculated using Coulomb's law. (1/(4πε₀)) is the inverse of Coulomb's constant. BQ and AQ are the distances from the +q and -q charges to point Q, respectively.
- VQ = VP q+ + VP q-: The total potential at point Q is the sum of the potentials due to each charge.
- VQ = q/(4πε₀) * [1/BQ - 1/AQ]: This is a simplified expression combining the above two equations.
- VQ = 0 :: BQ = AQ: On the equatorial plane, BQ and AQ are equal (BQ = AQ), resulting in a total potential VQ of 0. In other words, the electric potential at any point on the equatorial plane of a dipole is zero.
In summary, the image mathematically demonstrates that on the equatorial plane of a dipole, the potentials due to the two charges cancel each other out, resulting in a net potential of zero.
Note :
쌍극자의 적도면(equatorial plane)은 쌍극자를 이루는 두 점전하를 연결하는 선분(쌍극자 모멘트 벡터)에 수직이고, 그 선분의 중앙을 지나는 평면입니다. 쉽게 말해, 쌍극자의 중심을 지나고 쌍극자 모멘트 벡터와 직각을 이루는 평면입니다. 이 평면 상의 모든 점은 두 점전하로부터 같은 거리에 있지는 않지만, 두 점전하에 의해 만들어지는 전기장의 크기가 같고 방향이 반대이기 때문에, 그 합은 0이 되는 특징을 가지고 있습니다.