클라인-고든 방정식
Klein–Gordon equation

- 수식: (\Box + m^2)\phi = 0
- 설명: 1926년 오스카 클라인과 발터 고르단이 제안한 방정식으로, 상대론적 전자를 기술합니다.
- 특징: 슈뢰딩거 방정식의 상대론적 버전이며, 스칼라 장을 양자 연산자로 이해하는 데 기초가 되었습니다.
클라인-고든 방정식의 응용 분야은 무엇인가요?
클라인-고든 방정식은 다양한 분야에서 응용됩니다. 제공된 문서를 기반으로 클라인-고든 방정식의 응용 분야를 정리하면 다음과 같습니다.
- 상대론적 양자역학: 클라인-고든 방정식은 상대론적 양자역학에서 중요한 역할을 합니다[__LINK_ICON].
- 양자장론: 현대에는 상대성 이론을 기반으로 하는 장론에서 기본적인 스칼라 장을 기술하는 방정식으로 해석되며, 양자장론 등에서
활용됩니다[__LINK_ICON].
- 헬름홀츠 방정식: k^2 = -m^2이 음수일 때, 헬름홀츠 방정식은 클라인-고든 방정식이 됩니다[__LINK_ICON].
클라인-고든 방정식은 어떤 물리적 현상을 기술하나요?
클라인-고든 방정식은 주로 다음과 같은 물리적 현상을 기술합니다.
- 상대론적 자유 입자: 스핀이 없는(스핀-0) 상대론적 자유 입자를 기술하는 데 사용됩니다. 예를 들어, 힉스 입자와 같은 스칼라 입자를 기술할 수 있습니다.
- 상대론적 양자장론: 스칼라 장을 기술하는 데 사용됩니다. 양자장론에서는 입자를 장의 양자화된 형태로 보기 때문에, 클라인-고든 방정식은 스칼라 장의 운동을 기술하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다.
- 우주론: 초기 우주에서 인플레이션과 관련된 스칼라 장의 진화를 기술하는 데 사용될 수 있습니다.
클라인-고든 방정식은 상대론적 효과를 고려한 양자역학적 기술에 필수적이며, 다양한 물리적 현상을 이해하는 데 중요한 도구로 사용됩니다.
힉스 입자는 어떤 힘과 관련될까요?
힉스 입자는 전자기력, 약력, 강력 중 약력과 관련이 있습니다.
- 힉스 입자는 힉스 메커니즘을 통해 W 및 Z 보존과 같은 약력 매개 입자에 질량을 부여하는 역할을 합니다.
힉스 입자는 어떤 입자의 질량을 부여하나요?
힉스 입자는 다음과 같은 입자들의 질량을 부여하는 데 관여합니다.
- 기본 입자:
- 쿼크: 위 쿼크, 아래 쿼크, charm 쿼크, strange 쿼크, top 쿼크, bottom 쿼크
- 렙톤: 전자, 뮤온, 타우 입자, 그리고 각 입자에 대응하는 중성미자 (electron neutrino, muon neutrino, tau neutrino)
- 게이지 보손: W 보손과 Z 보손 (전자기력을 매개하는 광자는 질량이 없음)
- 복합 입자:
- 양성자 및 중성자와 같은 핵자 (쿼크와 글루온으로 구성)
힉스 메커니즘을 통해 힉스 입자는 다른 입자들과 상호작용하며, 이 상호작용의 결과로 입자들이 질량을 가지게 됩니다. 힉스 입자는 질량의 기원을 설명하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다.
힉스 입자가 질량을 부여하는 방식은 무엇인가요?
힉스 입자가 질량을 부여하는 방식은 힉스 메커니즘을 통해 설명됩니다. 힉스 메커니즘은 다음과 같은 단계로 이루어집니다.
1. 힉스 장: 우주에는 힉스 장이라는 특정한 장이 존재합니다. 이 힉스 장은 모든 공간에 균일하게 퍼져 있으며, 0이 아닌 값을 가집니다.
2. 자발적 대칭 깨짐: 힉스 장은 특정한 포텐셜 에너지를 가지며, 이 포텐셜 에너지가 최소가 되는 지점이 0이 아닌 값을 가집니다. 이러한 현상을 자발적 대칭 깨짐이라고 합니다. 자발적 대칭 깨짐으로 인해 힉스 장은 진공 기댓값을 가지게 됩니다.
3. 입자와 힉스 장의 상호작용: 다른 기본 입자들은 힉스 장과 상호작용합니다. 이 상호작용의 강도에 따라 입자가 가지는 질량이 결정됩니다. 힉스 장과 강하게 상호작용하는 입자는 큰 질량을 가지게 되고, 약하게 상호작용하는 입자는 작은 질량을 가지게 됩니다.
4. 힉스 입자의 등장: 힉스 장의 진동이 힉스 입자로 나타납니다. 힉스 입자는 힉스 장의 양자화된 형태로 볼 수 있습니다.
요약하자면, 힉스 입자는 힉스 장과의 상호작용을 통해 다른 입자들에게 질량을 부여합니다. 입자가 힉스 장을 "통과"할 때, 힉스 장과의 상호작용이 클수록 더 큰 질량을 가지게 됩니다. 마치 끈적한 시럽 속을 움직이는 것과 같이, 힉스 장은 입자의 운동을 방해하여 질량으로 나타나게 합니다.
힉스 장은 어떻게 만들어지나요?
제공된 문서에서 힉스 장이 어떻게 만들어지는지에 대한 직접적인 설명은 찾을 수 없었습니다. 하지만 힉스 입자와 힉스 장에 대한 정보를 바탕으로 추론할 수 있습니다.
- 힉스 장의 형성: 힉스 입자는 힉스 장을 형성하고, 힉스 장과 상호 작용하는 물체는 질량을 가지게 된다고 합니다. 모든 물질에 질량을 부여하는 것이 힉스 장이고, 힉스 장을 매개하는 것이 힉스 입자로 보는 것입니다[__LINK_ICON].
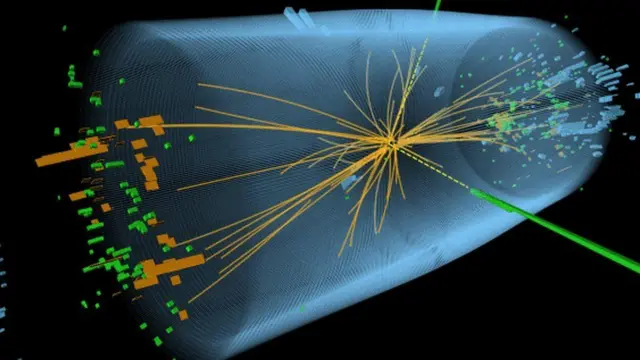
- 힉스 입자의 발견: 힉스 입자는 CERN(유럽 핵 연구 기구)의 대형 강입자 충돌기(LHC)에서 양성자 빔을 충돌시켜 만들어집니다. 이러한 충돌은 힉스 보손을 포함하여 많은 수의 아 원자 입자를 생성하며, 물리학자들은 이러한 충돌의 산물을 감지하고 분석함으로써 힉스 보손의 존재를 식별할 수 있습니다[__LINK_ICON].
힉스 장은 우주에 기본적으로 존재하는 장이며, 힉스 입자는 이 장의 양자화된 형태로 이해할 수 있습니다. 힉스 입자는 LHC와 같은 입자 가속기에서 고에너지 충돌을 통해 만들어지지만, 힉스 장 자체는 이러한 방식으로 "만들어지는" 것이 아니라 우주에 원래부터 존재하는 것으로 여겨집니다. : CIciAI
힉스 장은 어떤 곳에 존재하나요?
힉스 장은 우주 공간 어디에나 존재한다고 볼 수 있습니다[__LINK_ICON].
English translation:
Klein–Gordon equation

- Formula: (\Box + m^2)\phi = 0
- Description: An equation proposed by Oscar Klein and Walter Gordan in 1926, describing relativistic electrons.
- Features: Relativistic version of the Schrödinger equation, which was the basis for understanding scalar fields as quantum operators.
What are the applications of the Klein–Gordon equation?
The Klein–Gordon equation has applications in various fields. Based on the documents provided, the following is a summary of the applications of the Klein–Gordon equation:
- Relativistic quantum mechanics: The Klein–Gordon equation plays an important role in relativistic quantum mechanics [__LINK_ICON].
- Quantum field theory: In modern times, field theory based on relativity is interpreted as an equation describing the basic scalar field, and in quantum field theory, etc.
It is utilized [__LINK_ICON].
- Helmholtz equation: When k^2 = -m^2 is negative, Helmholtz equation becomes Klein-Gordon equation [__LINK_ICON].
What physical phenomena does the Klein–Gordon equation describe?
The Klein–Gordon equation primarily describes the following physical phenomena:
- Relativistic free particles: used to describe spin-free (spin-0) relativistic free particles. For example, scalar particles such as Higgs particles can be described.
- Relativistic quantum field theory: used to describe scalar fields. In quantum field theory, particles are viewed as quantized forms of fields, which is why the Klein–Gordon equation plays a crucial role in describing the motion of scalar fields.
- Cosmology: It can be used to describe the evolution of scalar fields associated with inflation in the early universe.
The Klein–Gordon equation is essential for quantum mechanical techniques that take into account relativistic effects and serves as a crucial tool in understanding various physical phenomena.
What force does the Higgs particle relate to?
Higgs particles are associated with electromagnetic, weak, and weak forces among strong forces.
- Higgs particles serve to impart mass to weak force mediated particles such as W and Z conservation through the Higgs mechanism.
What particle mass does the Higgs particle give?
Higgs particles are involved in imparting the mass of the following particles:
- Basic particles:
- Quark: Up quark, down quark, charm quark, strange quark, top quark, bottom quark
- Lepton: Electrons, muons, tau particles, and neutrinos corresponding to each particle (electron neutrino, muon neutrino, tau neutrino)
- Gauge boson: W boson and Z boson (photons mediating electromagnetic force have no mass)
- Composite particles:
- Nucleons such as protons and neutrons (composed of quarks and gluons)
Through the Higgs mechanism, Higgs particles interact with other particles, which result in particles having mass. Higgs particles play a crucial role in explaining the origin of mass.
How does a Higgs particle impart mass?
The way Higgs particles impart mass is explained by the Higgs mechanism. The Higgs mechanism consists of the following steps:
1. Higgs field: There is a specific field in the universe called Higgs field. This Higgs field is uniformly spread across all spaces, with nonzero values.
2. Spontaneous symmetry breaking: The Higgs field has a specific potential energy, and the point at which this potential energy becomes minimal has a nonzero value. This phenomenon is called spontaneous symmetry breaking. Due to spontaneous symmetry breaking, the Higgs field will have a vacuum expectation value.
3. Interaction of particles with Higgs field: Other elementary particles interact with Higgs field. The strength of this interaction determines the mass of the particles. Particles that interact strongly with the Higgs field will have a large mass, while particles that interact weakly will have a small mass.
4. Appearance of Higgs particles: The vibrations of the Higgs field appear as Higgs particles. Higgs particles can be viewed as quantized forms of Higgs fields.
In summary, the Higgs particle imparts mass to other particles through interaction with the Higgs field. When a particle "passes" through the Higgs field, the greater the interaction with the Higgs field, the greater the mass. Like moving through a sticky syrup, the Higgs field disrupts the motion of particles, causing them to appear as masses.
How is the Higgs chapter made?
From the documents provided, no direct explanation could be found of how the Higgs chapter is created. But you can deduce based on information about the Higgs particle and the Higgs field.
- Formation of the Higgs field: It is said that Higgs particles form the Higgs field, and objects interacting with the Higgs field have mass. It is the Higgs field that gives mass to all matter, and it is the Higgs particle that mediates the Higgs field [__LINK_ICON].
- Discovery of Higgs particles: Higgs particles are created by colliding a proton beam in a large hadron collider (LHC) at CERN (European Nuclear Research Organization). These collisions produce large numbers of subatomic particles, including the Higgs boson, and physicists can identify the presence of the Higgs boson by detecting and analyzing the products of these collisions [__LINK_ICON].
The Higgs field is a fundamental field in the universe, and the Higgs particle can be understood as a quantized form of this field. Higgs particles are created through high energy collisions in particle accelerators such as LHC, but the Higgs field itself is "made" in this way. It is not considered to exist in the universe from the beginning. : CIciAI
Where does the Hicks chapter exist?
The Higgs field can be seen as existing everywhere in outer space [__LINK_ICON].
Find out more about it.
Editorial Bridge of Love and Compassion