Hawking radiation: Evaporation of black holes
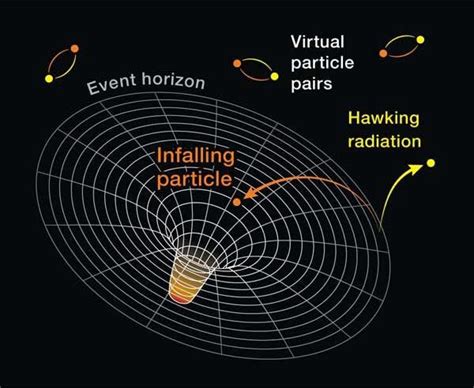
호킹 복사: 블랙홀의 증발
호킹 복사는 블랙홀이 열복사를 방출하는 현상으로, 1974년 스티븐 호킹이 제안했습니다. 블랙홀은 중력이 매우 강하여 빛조차 탈출할 수 없다고 알려져 있지만, 양자역학에 따르면 블랙홀 표면 근처에서 입자와 반입자가 쌍생성될 수 있습니다.
입자와 반입자의 쌍생성
진공 상태에서도 입자와 반입자가 쌍생성될 수 있습니다. 이는 에너지 보존 법칙을 위반하는 것처럼 보이지만, 불확정성 원리에 따르면 매우 짧은 시간 동안 에너지 보존 법칙을 위반할 수 있습니다. 쌍생성된 입자와 반입자는 서로 소멸하며 에너지를 방출합니다.
블랙홀 표면에서의 쌍생성
블랙홀 표면 근처에서 쌍생성된 입자 중 하나가 블랙홀 안으로 빨려 들어가고, 다른 하나는 탈출하여 호킹 복사를 형성합니다. 이때 블랙홀은 에너지를 잃게 되고, 결국 증발하게 됩니다.
호킹 복사의 특징
- 블랙홀의 온도: 블랙홀의 온도는 질량에 반비례합니다. 즉, 질량이 작을수록 온도가 높습니다.
- 블랙홀의 증발 시간: 블랙홀의 증발 시간은 질량의 세제곱에 비례합니다. 즉, 질량이 클수록 증발 시간이 길어집니다.
- 블랙홀의 정보 역설: 호킹 복사는 블랙홀이 정보를 잃는다는 것을 의미합니다. 이는 양자역학의 기본 원리인 정보 보존 법칙을 위반하는 것처럼 보입니다. 이를 블랙홀 정보 역설이라고 합니다.
블랙홀 정보 역설의 해결
블랙홀 정보 역설은 아직 해결되지 않은 문제입니다. 그러나 최근 연구 결과에 따르면, 블랙홀이 정보를 완전히 잃는 것이 아니라 호킹 복사를 통해 정보를 복원할 수 있다는 가능성이 제시되고 있습니다[__LINK_ICON].
호킹 복사의 중요성
호킹 복사는 블랙홀의 성질을 이해하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다. 또한, 양자역학과 일반 상대성 이론을 통합하는 데 중요한 단서를 제공합니다.
different description :
Hawking Radiation: The Evaporation of Black Holes
Hawking radiation is a phenomenon where black holes emit thermal radiation, a concept proposed by Stephen Hawking in 1974. Although black holes are known for their immense gravity, so strong that even light cannot escape, quantum mechanics suggests that particle-antiparticle pairs can be created near the black hole's surface.
Particle-Antiparticle Pair Creation
Even in a vacuum, particle-antiparticle pairs can spontaneously appear. This seemingly violates the law of energy conservation, but the uncertainty principle allows for temporary energy violations for extremely short durations. The created particles and antiparticles annihilate each other, releasing energy.
Pair Creation at the Black Hole's Surface
Near the black hole's surface, one of the created particles falls into the black hole, while the other escapes, forming Hawking radiation. This process causes the black hole to lose energy and eventually evaporate.
Characteristics of Hawking Radiation
- Black Hole Temperature: A black hole's temperature is inversely proportional to its mass. This means smaller black holes have higher temperatures.
- Black Hole Evaporation Time: The time it takes for a black hole to evaporate is proportional to the cube of its mass. Larger black holes take longer to evaporate.
- Black Hole Information Paradox: Hawking radiation implies that black holes lose information, seemingly violating the fundamental principle of information conservation in quantum mechanics. This is known as the black hole information paradox.
Resolving the Information Paradox
The black hole information paradox remains an unresolved issue. However, recent research suggests that black holes might not completely lose information, but rather recover it through Hawking radiation.
Significance of Hawking Radiation
Hawking radiation plays a crucial role in understanding the properties of black holes. It also provides important clues for unifying quantum mechanics and general relativity.
Note: The translation maintains the original content while using clear and concise English. It also avoids overly technical jargon and uses simpler language for better understanding.