이 행렬식들는 미적분학에서 **야코비 행렬식 (Jacobian Determinant), 헤시안 행렬식 (Hessian Determinant), 그리고 론스키안 행렬식 (Wronskian Determinant)**에 대한 정의와 공식을 보여줍니다. 각각의 개념은 다음과 같이 설명할 수 있습니다.
1. 야코비 행렬식 (Jacobian Determinant):
- 정의: 여러 변수 함수의 편도함수들로 구성된 행렬의 행렬식입니다. n 개의 변수를 가진 n 개의 함수가 있을 때, 각 함수의 각 변수에 대한 편도함수를 행렬로 배열하고, 그 행렬의 행렬식을 야코비 행렬식이라고 합니다.
- 용도: 다변수 함수의 변수 변환, 역함수 정리, 최적화 문제 등에서 중요하게 사용됩니다. 변수 변환 시 적분을 계산할 때 야코비 행렬식을 사용하여 적분 범위를 변환합니다.
- 공식: 이미지에 제시된 행렬식 공식을 참조하십시오. 각 ∂fᵢ/∂xⱼ 는 함수 fᵢ 를 변수 xⱼ 에 대해 편미분한 값을 나타냅니다.
2. 헤시안 행렬식 (Hessian Determinant):
- 정의: 여러 변수 함수의 2계 편도함수들로 구성된 행렬의 행렬식입니다. 함수의 모든 2계 편도함수를 행렬로 배열하고, 그 행렬의 행렬식을 헤시안 행렬식이라고 합니다.
- 용도: 함수의 국소적 최대값, 최소값, 안장점을 판별하는 데 사용됩니다. 헤시안 행렬의 고유값을 통해 함수의 곡률 정보를 얻을 수 있습니다.
- 공식: 이미지에 제시된 행렬식 공식을 참조하십시오. 각 ∂²φ/∂xᵢ∂xⱼ 는 함수 φ 를 변수 xᵢ 와 xⱼ 에 대해 이계 편미분한 값을 나타냅니다.
3. 론스키안 행렬식 (Wronskian Determinant):
- 정의: n 개의 함수가 선형 독립인지 판별하는 데 사용되는 행렬식입니다. 각 함수와 그 도함수들을 행렬로 배열하고, 그 행렬의 행렬식을 론스키안 행렬식이라고 합니다. 만약 론스키안 행렬식이 0이 아니면 함수들은 선형 독립입니다.
- 용도: 미분방정식의 해의 선형 독립성 판별, 함수의 선형 종속성 검정 등에 사용됩니다.
- 공식: 이미지에 제시된 행렬식 공식을 참조하십시오. fᵢ⁽ᵏ⁾ 는 함수 fᵢ 의 k 계 도함수를 나타냅니다.
요약하자면, 이 이미지는 다변수 미적분학에서 중요한 세 가지 행렬식의 정의와 공식을 요약하여 제시하고 있습니다. 이러한 행렬식들은 다양한 수학적 문제를 해결하는 데 필수적인 도구입니다.
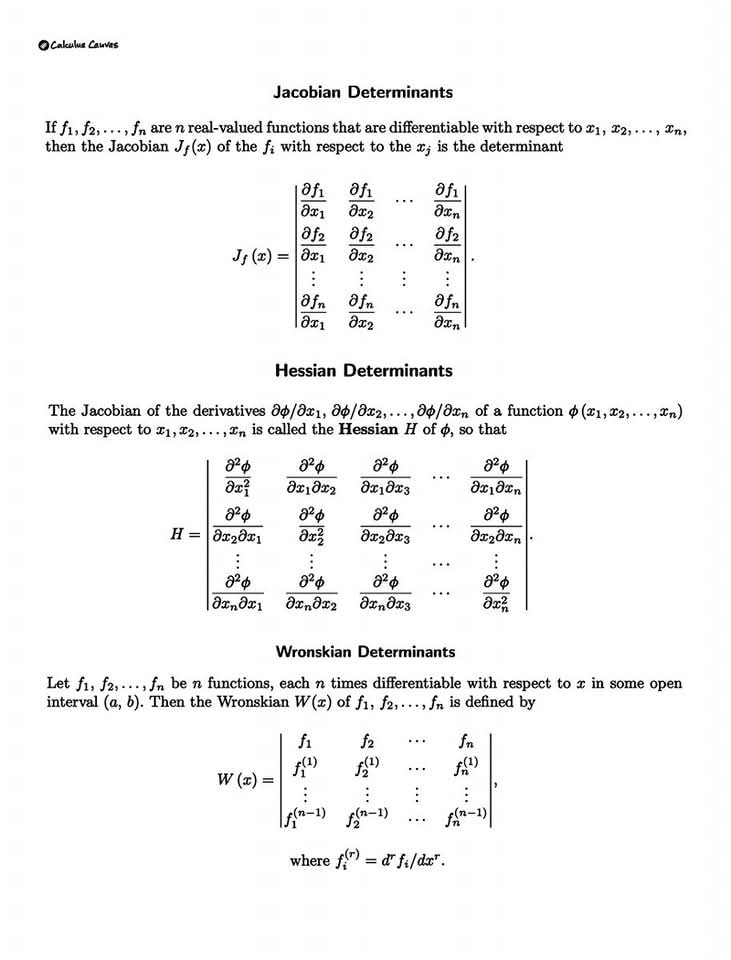
This image presents definitions and formulas for three important determinants in multivariable calculus: the Jacobian determinant, the Hessian determinant, and the Wronskian determinant. Each concept is explained below:
1. Jacobian Determinant:
- Definition: The determinant of a matrix composed of the partial derivatives of a system of functions. Given n functions of n variables, the Jacobian determinant is the determinant of the matrix where each entry is the partial derivative of one function with respect to one variable.
- Uses: Crucial in multivariable calculus for variable transformations (especially in integration), the inverse function theorem, and optimization problems. It's used to change the integration bounds when transforming variables in an integral.
- Formula: Refer to the matrix formula provided in the image. Each ∂fᵢ/∂xⱼ represents the partial derivative of function fᵢ with respect to variable xⱼ .
2. Hessian Determinant:
- Definition: The determinant of a matrix composed of the second-order partial derivatives of a function. All second-order partial derivatives of the function are arranged in a matrix, and its determinant is the Hessian determinant.
- Uses: Used to determine local maxima, minima, and saddle points of a function. The eigenvalues of the Hessian matrix provide information about the curvature of the function.
- Formula: Refer to the matrix formula in the image. Each ∂²φ/∂xᵢ∂xⱼ represents the second-order partial derivative of function φ with respect to variables xᵢ and xⱼ .
3. Wronskian Determinant:
- Definition: A determinant used to determine the linear independence of a set of functions. The functions and their derivatives are arranged in a matrix, and its determinant is the Wronskian determinant. If the Wronskian is non-zero, the functions are linearly independent.
- Uses: Determining the linear independence of solutions to differential equations, and testing for linear dependence of functions.
- Formula: Refer to the matrix formula in the image. fᵢ⁽ᵏ⁾ represents the kth derivative of function fᵢ .
In summary, this image summarizes the definitions and formulas for three crucial determinants in multivariable calculus. These determinants are essential tools for solving various mathematical problems.