Schwarzschild Metric (슈바르츠실트 메트릭)
아래 이미지는 **슈바르츠실트 메트릭(Schwarzschild Metric)**을 시각적으로 그리고 수학적으로 보여줍니다. 일반 상대성 이론에서 중력을 시공간의 곡률로 설명하는데, 슈바르츠실트 메트릭은 구형 대칭의 질량을 가진 천체 주변의 시공간의 기하학적 구조를 기술하는 메트릭입니다.
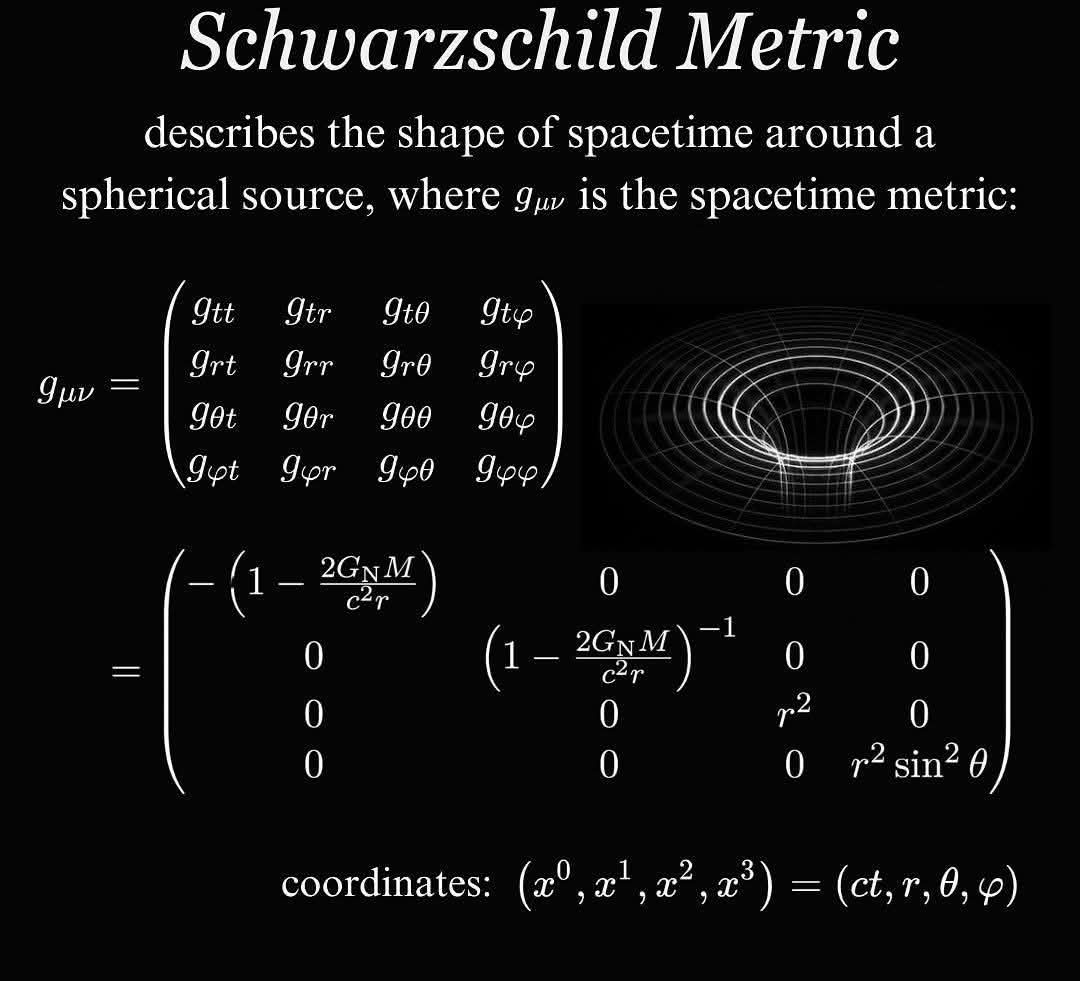
이미지 해설:
- 제목: "Schwarzschild Metric" 이라는 제목은 이 이미지가 슈바르츠실트 메트릭을 다룬다는 것을 명확히 합니다.
- 설명: "describes the shape of spacetime around a spherical source, where gμν is the spacetime metric" 이라는 설명은 슈바르츠실트 메트릭이 구형 질량 분포 주변의 시공간의 형태를 나타내는 메트릭임을 밝히고 있습니다. gμν는 시공간 메트릭 텐서를 나타냅니다.
- 메트릭 텐서: 4x4 행렬 형태로 표현된 gμν는 슈바르츠실트 메트릭 텐서입니다. 이 텐서는 시공간의 기하학적 성질을 담고 있으며, 시공간의 거리와 간격을 계산하는 데 사용됩니다. 행렬의 각 요소는 특정 좌표계에서 시공간의 곡률을 나타냅니다.
- 수식: 메트릭 텐서의 각 요소는 다음과 같이 주어집니다.

여기서:
- G: 중력 상수
- N: 질량
- c: 광속
- r: 천체 중심으로부터의 거리
- θ: 천체 중심으로부터의 위도
- φ: 천체 중심으로부터의 경도
- 좌표계: "(x0, x1, x2, x3) = (ct, r, θ, φ)" 는 사용된 좌표계를 나타냅니다. ct는 시간 좌표 (c는 광속, t는 시간), r은 반지름, θ는 극각, φ는 방위각입니다.
- 시각적 표현: 오른쪽의 그림은 슈바르츠실트 메트릭에 의해 묘사되는 시공간의 곡률을 시각적으로 나타냅니다. 천체의 중력에 의해 시공간이 휘어지는 모습을 보여줍니다. 중심부의 깊은 우물은 블랙홀의 특이점(singularity)을 상징적으로 나타낼 수 있습니다.
결론:
이 이미지는 슈바르츠실트 메트릭의 수학적 표현과 그 기하학적 의미를 함께 보여주는 효과적인 시각 자료입니다. 일반 상대성 이론의 중요한 개념인 시공간의 곡률과 블랙홀의 개념을 이해하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
https://youtu.be/NAXFFiioCcc
The image visually and mathematically illustrates the Schwarzschild Metric. In general relativity, gravity is described as the curvature of spacetime, and the Schwarzschild metric is a metric that describes the geometry of spacetime around a spherically symmetric object with mass.
Image Explanation:
- Title: The title "Schwarzschild Metric" clearly indicates that the image is about the Schwarzschild metric.
- Description: The description "describes the shape of spacetime around a spherical source, where gμν is the spacetime metric" clarifies that the Schwarzschild metric represents the shape of spacetime around a spherical mass distribution. gμν represents the spacetime metric tensor.
- Metric Tensor: The 4x4 matrix shown as gμν is the Schwarzschild metric tensor. This tensor encapsulates the geometrical properties of spacetime and is used to calculate distances and intervals within spacetime. Each element of the matrix represents the curvature of spacetime in a specific coordinate system.
- Equation: The elements of the metric tensor are given as follows:

Where:
- G: Gravitational constant
- M: Mass
- c: Speed of light
- r: Distance from the center of the object
- θ: Latitude from the center of the object
- φ: Longitude from the center of the object
- Coordinate System: "(x0, x1, x2, x3) = (ct, r, θ, φ)" represents the coordinate system used. ct is the time coordinate (c is the speed of light, t is time), r is the radius, θ is the polar angle, and φ is the azimuthal angle.
- Visual Representation: The image on the right visually depicts the curvature of spacetime as described by the Schwarzschild metric. It shows how spacetime is warped by the gravity of the object. The deep well in the center can be interpreted as a symbolic representation of the singularity of a black hole.
Conclusion:
This image effectively combines the mathematical expression and geometrical meaning of the Schwarzschild metric. It helps to understand key concepts in general relativity, such as the curvature of spacetime and the concept of black holes.