Geometric formula theorem
1. 직육면체 (Rectangular parallelepiped):
- 부피 (V): V = a·b·c (a, b, c는 각 변의 길이)
2. 직각기둥 (Straight prism):
- 부피 (V): V = S_base · h (S_base는 밑면의 넓이, h는 높이)
3. 피라미드 (Pyramid):
- 부피 (V): V = (1/3)S_base · h (S_base는 밑면의 넓이, h는 높이)
4. 원뿔 (Cone):
- 부피 (V): V = (1/3)πr²h (r은 밑면의 반지름, h는 높이)
- 옆면의 넓이: πrl (l은 모선의 길이)
5. 원기둥 (Cylinder):
- 부피 (V): V = πr²h (r은 밑면의 반지름, h는 높이)
- 옆면의 넓이: 2πrh
6. 구 (Sphere):
- 부피 (V): V = (4/3)πr³ (r은 반지름)
- 표면적 (S): S = 4πr²
7. 삼각형의 중선 (Middle line of the triangle):
- 중선의 길이: 밑변의 절반
8. 사다리꼴의 중선 (Middle line of the trapezoid):
- 중선의 길이: (윗변 + 아랫변) / 2
9. 피타고라스 정리 (Pythagorean theorem):
- a² + b² = c² (a, b는 직각삼각형의 두 직각변의 길이, c는 빗변의 길이)
10. 원 (Circle):
- 둘레 (Circumference): C = 2πr (r은 반지름)
- 넓이 (Area): S = πr²
11. 정삼각형 (Regular triangle):
- 반지름 (R): R = a√3 / 3 (a는 한 변의 길이)
- 넓이 (S): S = a²√3 / 4
12. 평행사변형 (Parallelogram):
- 넓이 (S): S = a·h (a는 밑변의 길이, h는 높이) 또는 S = a·b·sinγ (a, b는 두 변의 길이, γ는 두 변 사이의 각도)
13. 삼각형 (Triangle):
- 넓이 (S): S = (1/2)a·h (a는 밑변의 길이, h는 높이) 또는 S = (1/2)ab·sinγ (a, b는 두 변의 길이, γ는 두 변 사이의 각도)
14. 사다리꼴 (Trapeze):
- 넓이 (S): S = (a+b)h/2 (a, b는 평행한 두 변의 길이, h는 높이)
15. 마름모 (Rhombus):
- 넓이 (S): S = (1/2)d₁d₂ (d₁, d₂는 두 대각선의 길이)
이 이미지는 다양한 기하학 도형의 기본적인 면적과 부피 공식을 정리한 참고자료로 유용하게 사용될 수 있습니다. 각 공식의 유도 과정은 생략되어 있으므로, 필요하다면 별도로 확인해야 합니다.
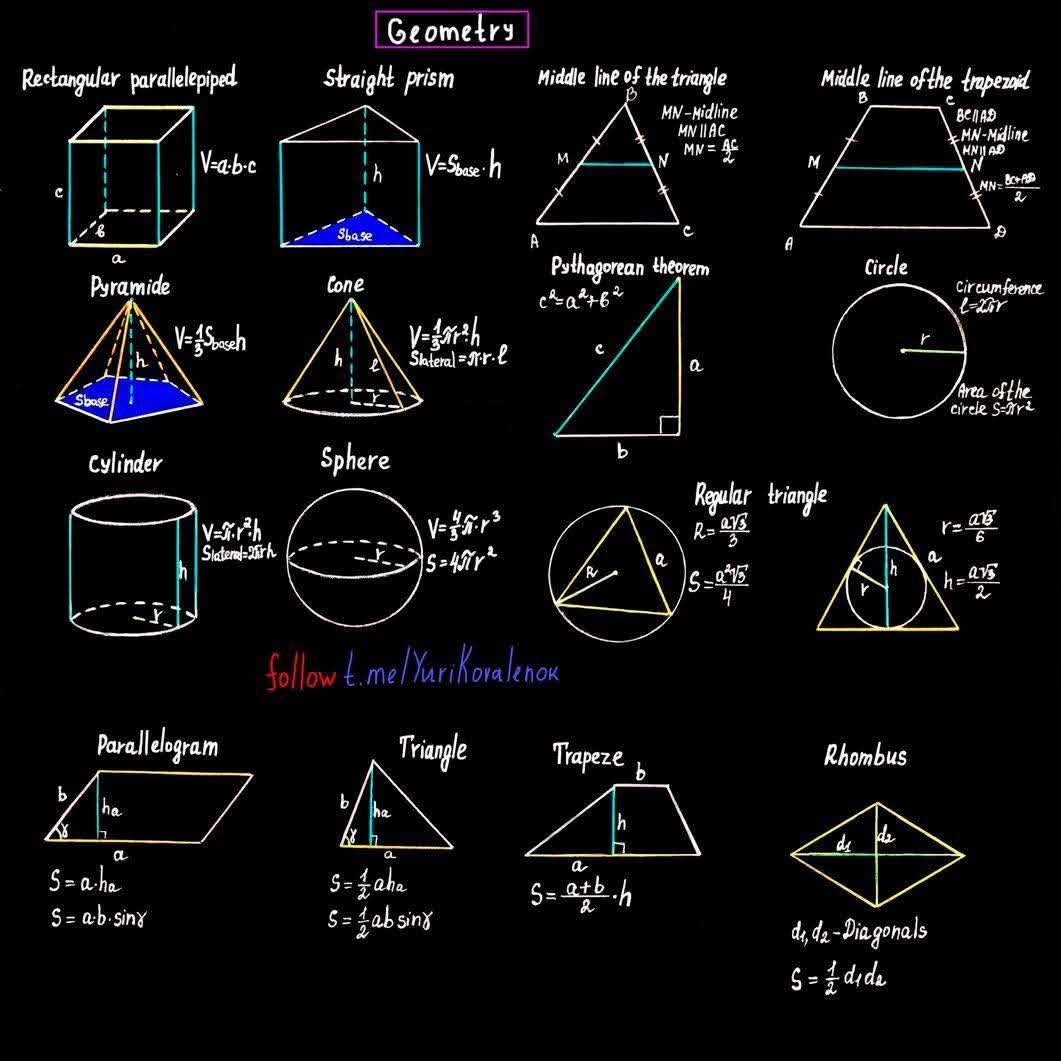
Geometric formula theorem
1. Rectangular parallelepiped:
- Volume (V): V = a·b·c (a, b, c are the lengths of each side)
2. Straight prism:
- Volume (V): V = S_base · h (S_base is the area of the base, h is the height)
3. Pyramid:
- Volume (V): V = (1/3)S_base · h (S_base is the area of the base, h is the height)
4. Cone:
- Volume (V): V = (1/3)πr²h (r is the radius of the base, h is the height)
- Lateral surface area: πrl (l is the slant height)
5. Cylinder:
- Volume (V): V = πr²h (r is the radius of the base, h is the height)
- Lateral surface area: 2πrh
6. Sphere:
- Volume (V): V = (4/3)πr³ (r is the radius)
- Surface area (S): S = 4πr²
7. Middle line of the triangle:
- Length of the middle line: Half the length of the base
8. Middle line of the trapezoid:
- Length of the middle line: (Top base + Bottom base) / 2
9. Pythagorean theorem:
- a² + b² = c² (a, b are the lengths of the two legs of a right triangle, c is the length of the hypotenuse)
10. Circle:
- Circumference: C = 2πr (r is the radius)
- Area: S = πr²
11. Regular triangle:
- Radius (R): R = a√3 / 3 (a is the length of a side)
- Area (S): S = a²√3 / 4
12. Parallelogram:
- Area (S): S = a·h (a is the length of the base, h is the height) or S = a·b·sinγ (a, b are the lengths of two sides, γ is the angle between them)
13. Triangle:
- Area (S): S = (1/2)a·h (a is the length of the base, h is the height) or S = (1/2)ab·sinγ (a, b are the lengths of two sides, γ is the angle between them)
14. Trapeze:
- Area (S): S = (a+b)h/2 (a, b are the lengths of the two parallel sides, h is the height)
15. Rhombus:
- Area (S): S = (1/2)d₁d₂ (d₁, d₂ are the lengths of the two diagonals)
This image serves as a useful reference for basic area and volume formulas for various geometric shapes. The derivation of each formula is omitted, so you may need to refer to other resources for that information.