Various organs of the digestive system
아래 그림은 소화계의 다양한 기관에서 일어나는 영양소 흡수 과정을 보여줍니다. 각 기관에서 어떤 영양소가 흡수되는지 간략하게 설명하겠습니다.
위 (Stomach): 단백질 소화가 시작되고, 철분 (Fe⁺⁺⁺)이 흡수됩니다. 펩신이 단백질을 분해하기 시작합니다. 내인성 인자(Intrinsic factor)는 비타민 B₁₂와 결합하여 흡수를 돕습니다.
십이지장 (Duodenum): 췌장에서 분비된 효소(아밀라아제, 프로테아제, 리파아제)가 작용하여 탄수화물, 단백질, 지방이 더 작은 분자로 분해됩니다. 아미노산이 흡수되고, 탄수화물(이당류)이 분해됩니다.
소장 (Jejunum & Ileum): 소장의 융털(villi)에서 영양소의 대부분이 흡수됩니다. 단당류, 모노글리세리드, 지방산, 비타민(지용성 및 수용성), 칼슘, 엽산 등이 흡수됩니다. 비타민 B₁₂는 회장(Ileum)에서 흡수됩니다. 물과 전해질도 흡수됩니다.
대장 (Colon): 물과 전해질이 소량 흡수됩니다. 담즙산은 간으로 재순환됩니다.
간 (Liver): 담즙을 생성하여 지방의 소화를 돕습니다.
췌장 (Pancreas): 소화 효소(아밀라아제, 프로테아제, 리파아제)를 분비하여 영양소의 분해를 촉진합니다.
그림에서 보이는 주요 영양소 흡수 과정:
- 단백질: 위에서 펩신에 의해 분해 시작, 십이지장에서 아미노산으로 분해 후 흡수.
- 탄수화물: 구강에서 아밀라아제에 의해 일부 분해, 십이지장에서 단당류로 분해 후 흡수.
- 지방: 십이지장에서 리파아제에 의해 분해, 모노글리세리드와 지방산으로 분해 후 흡수.
- 철분: 위에서 흡수.
- 비타민 B₁₂: 위에서 내인성 인자와 결합, 회장에서 흡수.
- 물 및 전해질: 소장과 대장에서 흡수.
- 지용성 비타민: 소장에서 흡수.
- 수용성 비타민: 소장에서 흡수.
- 칼슘: 소장에서 흡수.
- 엽산: 소장에서 흡수.
이 그림은 소화 과정의 개략적인 모습을 보여주는 것이며, 실제 소화 과정은 더욱 복잡합니다. 각 영양소의 흡수량은 다양한 요인에 따라 달라집니다.
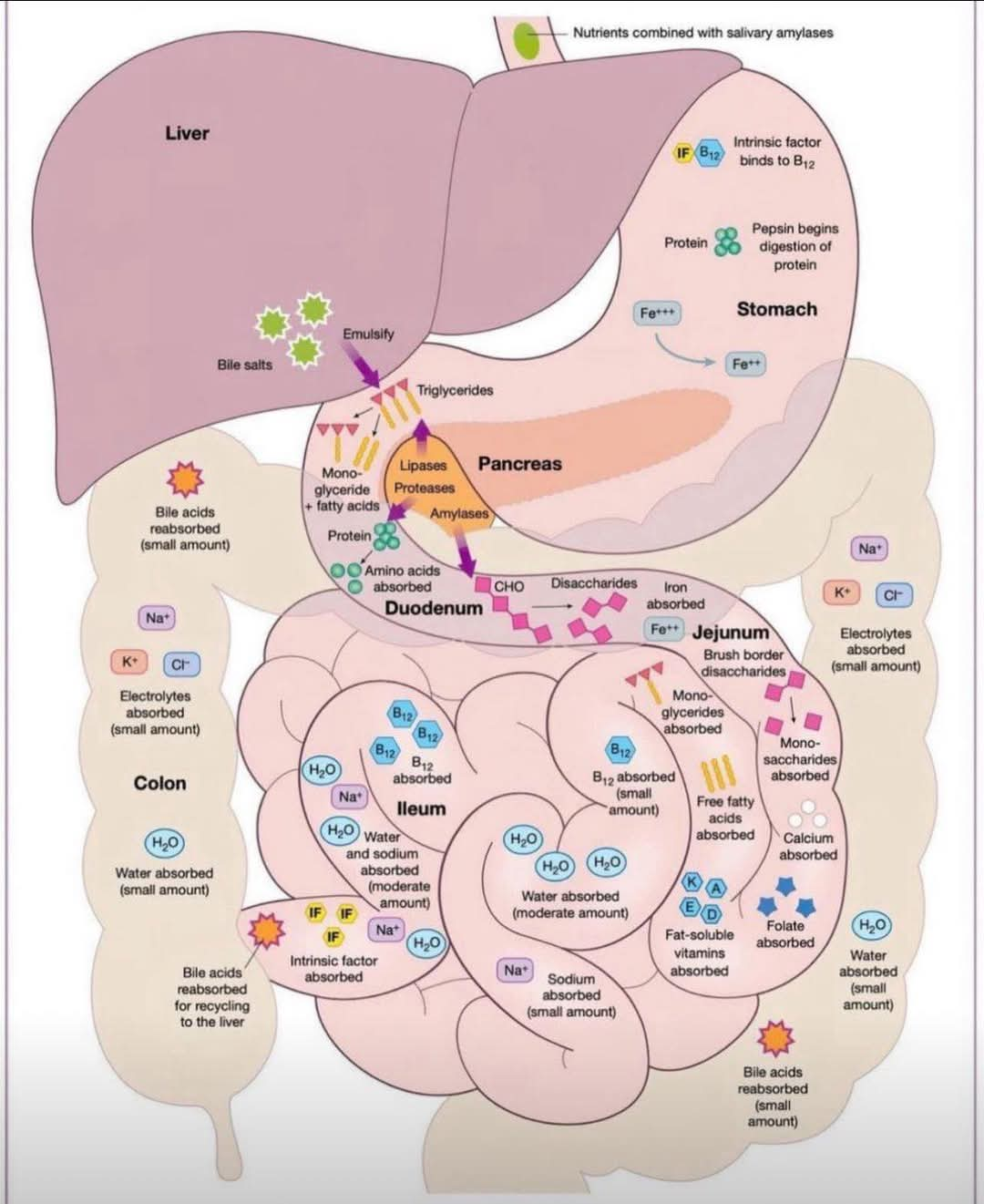
This figure shows the nutrient uptake processes that occur in different organs of the digestive system. Let me briefly explain which nutrients are absorbed by each organ.
Stomach: Protein digestion begins, iron (Fe+++) is taken up. Pepsin begins to break down proteins. Endogenous factor combines with vitamin B12 to help absorb.
Duodenum: Enzymes (amylases, proteases, lipases) secreted from the pancreas act, breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into smaller molecules. Amino acids are absorbed, and carbohydrates (disaccharides) are broken down.
Small intestine (Jejunum & Ileum): Most of the nutrients are absorbed from the villi of the small intestine. Monosaccharides, monoglycerides, fatty acids, vitamins (soluble and water soluble), calcium, folate, etc. are absorbed. Vitamin B12 is absorbed by the ileum. Water and electrolytes are also absorbed.
Colon: Water and electrolyte are absorbed in small amounts. Bile acids are recycled to the liver.
Liver: It helps digest fat by producing bile.
Pancreas: It secretes digestive enzymes (amylase, protease, lipase) to promote the breakdown of nutrients.
The major nutrient uptake processes shown in the figure:
- Protein: Begin degradation by pepsin in the stomach, take up after degradation to amino acids in the duodenum.
- Carbohydrates: Some degradation by amylase in the oral cavity, absorption after degradation by duodenum to monosaccharides.
- Fat: Degraded by lipase in the duodenum, and absorbed after degradation to monoglycerides and fatty acids.
- Iron: Absorption from the stomach.
- Vitamin B12: Binding with endogenous factors in the stomach, absorption in the ileum.
- Water and electrolytes: Absorption from the small and large intestine.
- Fat-soluble vitamins: Absorption from the small intestine.
- Water-soluble vitamins: Absorption from the small intestine.
- Calcium: Absorption from the small intestine.
- Folic acid: Absorption from the small intestine.
This figure shows a schematic view of the digestion process, and the actual digestion process is more complex. The absorption of each nutrient depends on various factors.