Geometry(기하학)
이 이미지는 기하학(Geometry)에서 원의 일부분에 대한 면적과 길이를 계산하는 공식들을 보여줍니다. 원의 반지름을 r , 중심각을 θ (라디안 단위)라고 할 때, 다음과 같은 공식들이 제시되어 있습니다:
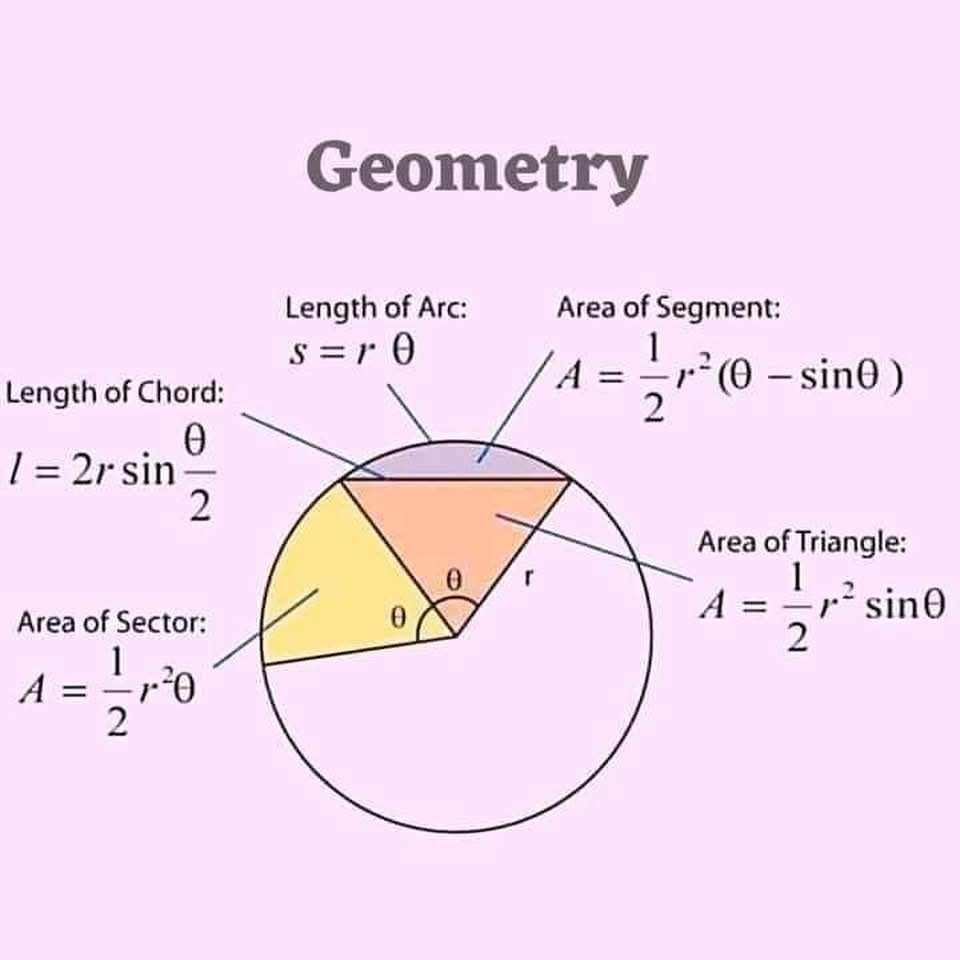
- 호의 길이 (Length of Arc): s = rθ - 반지름과 중심각의 곱으로 호의 길이를 구합니다.
- 현의 길이 (Length of Chord): l = 2r sin(θ/2) - 반지름과 중심각을 이용하여 현의 길이를 계산합니다.
- 부채꼴의 면적 (Area of Sector): A = (1/2)r²θ - 반지름의 제곱과 중심각의 곱에 1/2을 곱하여 부채꼴의 면적을 구합니다.
- 삼각형의 면적 (Area of Triangle): A = (1/2)r²sinθ - 반지름의 제곱과 중심각의 사인값에 1/2을 곱하여 삼각형의 면적을 계산합니다.
- 활꼴의 면적 (Area of Segment): A = (1/2)r²(θ - sinθ) - 부채꼴의 면적에서 삼각형의 면적을 빼서 활꼴(segment)의 면적을 구합니다.
이 이미지는 원의 기본적인 기하학적 성질과 관련된 공식들을 그림과 함께 간결하게 정리한 것입니다. 각 공식은 원의 반지름과 중심각을 이용하여 원의 일부분의 면적과 길이를 계산하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
이미지에 나온 공식들은 어디에 활용되나요?
이미지에 나온 공식들은 원과 관련된 다양한 분야에서 활용됩니다. 주요 활용 분야는 다음과 같습니다.
- 기하학 (Geometry): 원의 호의 길이, 현의 길이, 부채꼴, 삼각형, 활꼴의 면적을 계산하는 데 직접적으로 사용됩니다. 원에 내접하는 다각형의 면적이나 길이를 계산하는 문제를 푸는 데에도 활용될 수 있습니다.
- 삼각법 (Trigonometry): 현의 길이 공식은 삼각함수(sin)를 이용하므로 삼각법과 밀접한 관련이 있습니다. 원과 삼각함수의 관계를 이해하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다.
- 미적분학 (Calculus): 원호의 길이와 면적을 구하는 공식은 미적분학에서 곡선의 길이와 면적을 구하는 더 복잡한 문제를 푸는 기초가 됩니다. 극좌표계를 이용한 적분 계산에 응용될 수 있습니다.
- 공학 (Engineering): 원형 구조물이나 기계 설계, 건축 등에서 원의 일부분의 면적이나 길이를 계산해야 하는 경우 이 공식들이 활용됩니다. 예를 들어, 곡선 도로의 길이 계산이나 원형 파이프의 단면적 계산 등에 사용됩니다.
- 컴퓨터 그래픽스 (Computer Graphics): 컴퓨터 그래픽스에서 원이나 원호를 그리거나 원의 일부분을 표현할 때 이 공식들이 사용됩니다. 게임이나 애니메이션 제작 등에 활용됩니다.
- 물리학 (Physics): 원운동이나 파동 등을 다루는 물리학 문제에서 원의 호의 길이, 각속도 등을 계산하는 데 사용될 수 있습니다.
요약하자면, 이 공식들은 수학의 여러 분야뿐 아니라 공학, 컴퓨터 그래픽스, 물리학 등 다양한 분야에서 원과 관련된 문제를 해결하는 데 기본적인 도구로 사용됩니다. 원은 자연 현상과 인공 구조물에서 흔히 나타나는 형태이기 때문에 이러한 공식들의 활용 범위는 매우 넓습니다.
Geometry (geometry)
This image shows formulas for calculating the area and length of a part of a circle in geometry. When the radius of the circle is r and the central angle is θ (in radian), the following formulas are presented:

- Length of Arc: s = rθ - Find the length of the arc by the product of radius and central angle.
- Length of Chord: l = 2r sin(θ/2) - Calculate the length of the chord using radius and center angle.
- Area of Sector: A = (1/2)r2θ - Multiply the product of the square of the radius and the central angle by 1/2 to obtain the area of the fan.
- Area of Triangle: A = (1/2)r2sinθ - Calculate the area of the triangle by multiplying the square of the radius and the sine value of the center angle by 1/2.
- Area of Segment: A = (1/2)r2(θ - sinθ) - Subtract the area of the triangle from the area of the fan to obtain the area of the segment.
This image is a concise summary of the formulas related to the basic geometric properties of a circle along with the picture. Each formula illustrates how to calculate the area and length of a part of a circle using the radius and center angle of the circle.
Where are the formulas in the image used?
The formulas in the image are utilized in various fields related to circles. The main areas of use are:
- Geometry: It is used directly to calculate the area of arc length of a circle, string length, fan shape, triangle, and archetype. It can also be used to solve problems in calculating the area or length of a polygon inscribed in a circle.
- Trigonometry: The string length formula is closely related to trigonometry because it uses trigonometric functions (sin). It plays a crucial role in understanding the relationship between circles and trigonometric functions.
- Calculus: The formula for finding the length and area of an arc is the basis for solving the more complex problem of finding the length and area of a curve in calculus. It can be applied to integral calculations using polar coordinates.
- Engineering: These formulas are used when you need to calculate the area or length of a part of a circle in a circular structure, mechanical design, architecture, etc. For example, it is used for calculating the length of curved roads or calculating the cross-sectional area of circular pipes.
- Computer Graphics: These formulas are used in computer graphics to draw circles or arcs or express parts of circles. It is used for games and animation production.
- Physics: It can be used to calculate the length, angular velocity, etc. of an arc in a circle in physics problems dealing with circular motion or waves.
In summary, these formulas are used as basic tools to solve circle-related problems in various fields such as engineering, computer graphics, and physics as well as various fields of mathematics. Since circles are common forms in natural phenomena and artificial structures, the scope of use of these formulas is very wide.